Decoding Urban Green Spaces: Deep Learning and Google Street View Measure Green Structures
Abstract
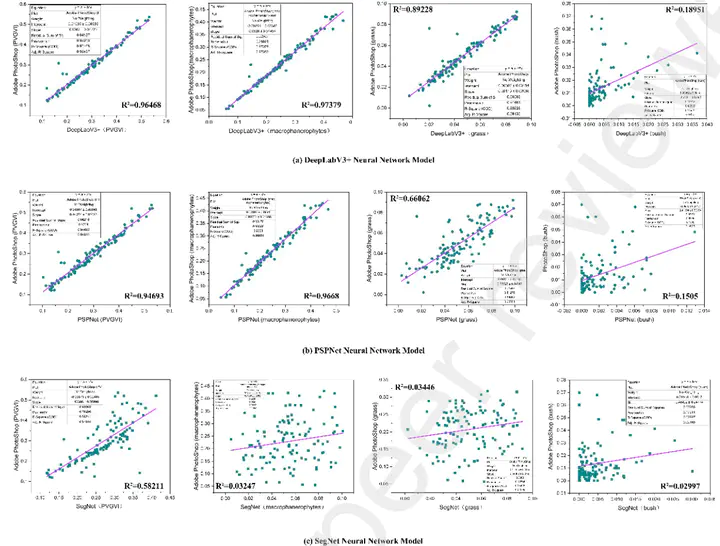
Street greenery is an extremely important component in urban ecological quality assessment, and panoramic street images can represent the street landscape more comprehensively. Many studies have shown that street greenery is highly correlated with the physical and mental health of urban residents, and exploring the diverse composition of street greenery is also an important indicator to explain the health mechanism. In this study, we propose a method based on semantic segmentation of panoramic street images to assess the structure of urban street greenery and calculate the proportion of various types of plants in the urban street green landscape. For this purpose, we constructed a new streetscape dataset S-G-S-S (Street Greening Space Structure Dataset) , which is dedicated to urban research. Based on this, DeepLabV3+ neural network models are trained to semantically segment the panoramic streetscape images with the aim of improving the accuracy while accurately identifying the street greening structures. To verify the accuracy and stability of the method, an empirical study was conducted in the Livingston area of western New York City, USA, using multiple neural network models and comparing the results. The results show that the method can better visualize the green structure at the urban street level.